
Instrumental synthesis
Instrumental synthesis is a technique for composition and orchestration first developed in the 1970s. It is a founding principle of French spectral music, represented at that time mainly by the composers Tristan Murail, Hugues Dufourt, and Gérard Grisey. This type of compositional process could not have existed without the technological progress in musical acoustics made in the previous decades…
La synthèse instrumentale est une technique d’écriture et d’orchestration développée principalement dans les années 1970-1980. C’est le principe fondateur du courant de la musique spectrale, né en France et principalement représenté par les compositeurs Tristan Murail, Hugues Dufourt et Gérard Grisey à cette époque. Ce procédé compositionnel n’aurait pas pu exister sans les progrès technologiques en acoustique des dernières décennies.

Schnittke’s Concerto Grosso No. 1
Alfred Schnittke’s Concerto Grosso No. 1 (1977), composed at the height of his “polystylistic” period, is filled with diverse musical materials. The 28-minute piece is divided into six movements combining different musical genres, styles, and sonorities. As musicologist Maria Bergamo describes, “The musical ideas, the themes and motives of the work are linked in all six movements, gaining new interpretations and aspects by varied treatment and paraphrases.”[1] For this Amazing Moment in Timbre, I will describe the interaction of timbres in the second movement, the Toccata, focusing on two main timbral features: sound mass and textural integrations.
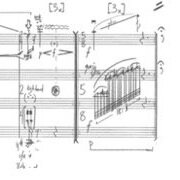
The children of fire come looking for fire — Eric Wubbels
As stated in the album liner notes for Eric Wubbels’s Duos with Piano Book I, “these pieces aim to develop a 21st-century conception of ensemble virtuosity (now a virtuosity of listening, concentration, timbral fusion, and collaborative decision-making as much as of technique) in the microcosm of the duo format.” “the children of fire come looking for fire” (2012), for violin and prepared piano, stays true to Wubbel’s stated aim not only in its inventive combination of similar gestures in differing instruments, but also in its use of these individual instruments to highlight the and forefront each other’s particular timbral qualities.

Brightness / Darkness
“Brightness” is one of the most common terms used to describe sounds, drawing on strong cross-modal associations. Most people can call to mind examples of “bright” sounds: what do these sounds have in common?
Most sounds are made up of multiple different sound components, including partials and noise components. The relations between sound components have a big impact on how the overall sound is perceived:

Seven Beginnings
Seven Beginnings (2019), for flute, oboe, clarinet, bassoon, horn, two violins, viola, and cello, was composed as a deliverable of my ACTOR postdoc. The piece builds upon the trend of speech transcription in recent music, with a focus on spectral transcription and cross-modal composition. But far from being a technical étude, it is a very personal piece with a very specific motivation behind its materials and methods.

Buzzard and Kestrel — James Blake
A snare drum pounds relentlessly for the first sixty seconds of James Blake’s “Buzzard and Kestrel,” punctuated by random swoops of vocoderised voices, the occasional handclap, and an intermittent sub-bass almost at the edge of hearing. As the drum pattern repeats again and again, its reverberation steadily grows until the entire track is blanketed in a continuous sizzle. At its peak, around 0:56, the drum’s attacks are almost completely swallowed by their own echoes, the reverb an unremitting rush in our ears…
Then, something amazing happens.

The Colour “Fresh”: Timbre in Intermezzo no. 1 — Yinam Leef
No doubt, a stirring sense of vitality captures you from the very first moment of this miniature. But what is it that is so captivating about this Intermezzo? Clearly, the composer focuses our attention on a very particular technique of orchestration that he uses throughout. Nevertheless, we don’t get tired of it: it stays fresh long after we recognize this particular orchestration as a main expressive element…

The Singer’s Formant
Have you ever wondered how opera singers sing so loudly? In the voice studio, operatic singing is not actually thought of as loud but rather as possessing resonance (in singers’ terms, not acousticians’ terms), focus (sometimes visualized as a laser point), cut (a non-technical term meaning the voice can cut through the texture of an orchestra), or squillo (an Italian word for the buzzy quality in an operatic voice). A classically trained voice can be heard despite being accompanied by strings, percussion, woodwinds, and, in the case of Wagner’s Die Walküre, twenty-two brass instruments.

Flourish — Sarah Hennies
From the very beginning of the piece, Sarah Hennies’s Flourish for two vibraphone players, leads us into an extraordinary, mystical, new world of sound. What is so enigmatic about this piece is that a lot of the music happens in a realm of timbre beyond what is written and what is played. Precisely and cleanly scored in minimalist fashion of single-measure repeating cells, the atmospheric reverberations produced by the vibraphone are here left to write their own counterpoint….

Inharmonicity
Inharmonicity is a feature of timbre that is related to the frequency spectrum of a given sound. It is measured through an analysis of the partials (see https://www.actorproject.org/timbreducation/timbre-term-of-the-week-1), or, more precisely, of their frequencies and the intervals between them….

The Unanswered Question – Charles Ives
In 1908, American composer Charles Ives composed The Unanswered Questionfor string orchestra, solo trumpet (or English Horn) and four flutes (or three oboes and one clarinet). This piece inspired Leonard Bernstein’s famous Norton Lectures of the same title at Harvard in 1973 and continues to capture the imaginations of musicians and audiences today….
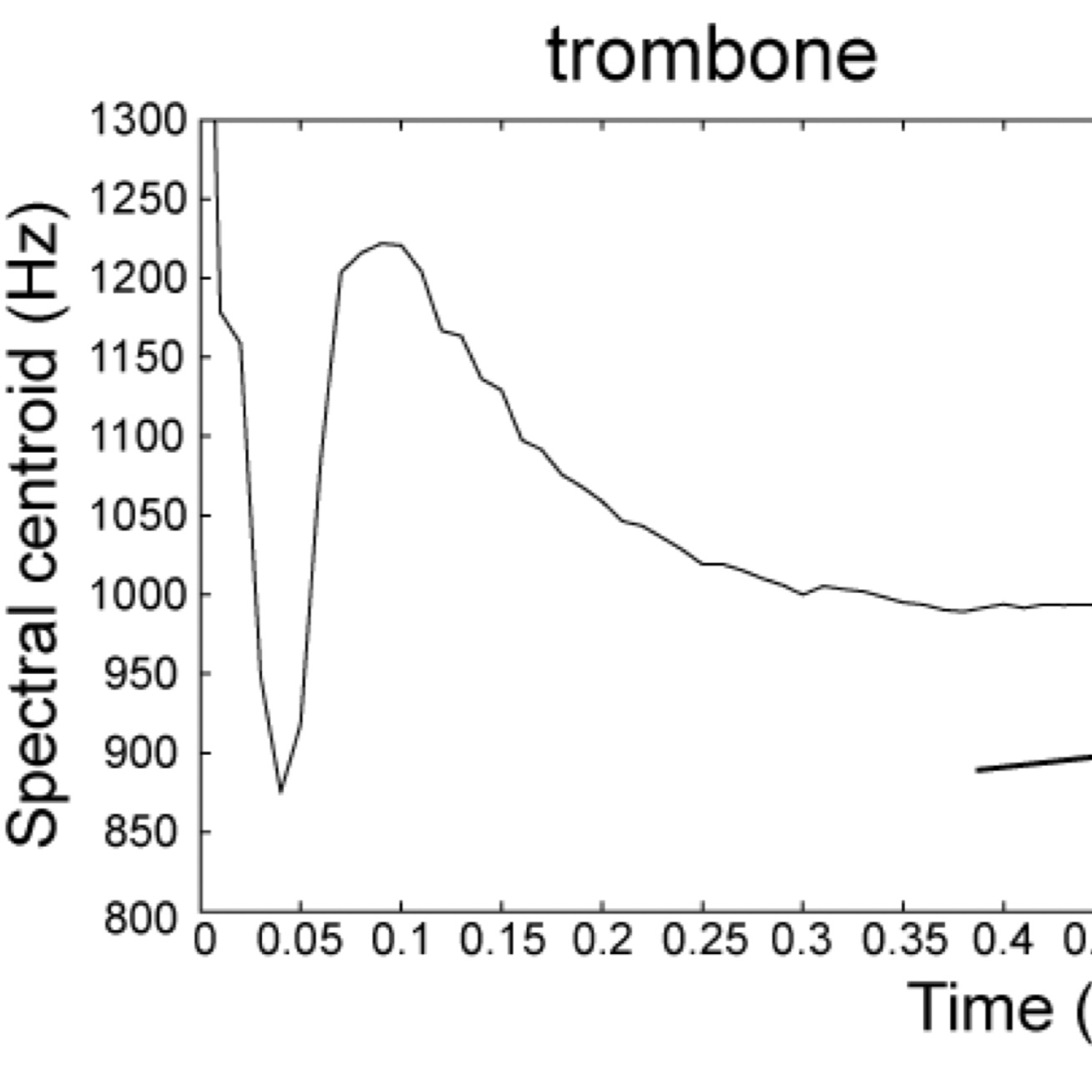
Spectral centroid
Spectral centroid is an acoustical descriptor of timbre. Its value is obtained through a statistical measurement on the frequency representation of the signal (the frequency spectrum - see Timbre Term of the Week "Signal vs Spectrum"). As its name says, centroid is a spectral descriptor and corresponds to a specific type of estimation of the spectral shape (or curve)…

Red Bird —Trevor Wishart
Trevor Wishart is a contemporary British composer closely associated with extended uses of the human voice. Whether in acousmatic pieces such as Encounters in the Republic of Heaven (2011) or in pieces for live performance such as Vox 4(1987), his compositions masterfully exploit the subtlety and range of human vocal production…

Menotti’s Goya and The Timbre of Tinnitus
When considering the compositional problem of Goya’s deafness, Gian Carlo Menotti may have struggled to find the best approach. However, forty years prior to the première of Goya (1986), he had already explored the issue of muteness …
Signal vs. Spectrum
In everyday life, sounds are captured by our auditory system and analyzed in our brains. But in order to better understand the physical phenomena that comes with sound production, we use analytical methods, both analog and computational, that are based on different representations of the sound vibration.

Hommage à Klaus Nomi
The Amazing Moments in Timbre series continue with a piece by Olga Neuwirth. Known as the "Enfant terrible" of the Austrian contemporary classical music scene, Neuwirth composes in a very theatrical and expressionist way, and describes her own art as a music of catastrophes ("Katastrophenmusik"). In her Hommage à Klaus Nomi(2009), for countertenor and chamber ensemble…
Shepard Tone
In this post Auditory Scene Analysis, we introduced some of the ways that sound components are grouped together by the auditory system. This has many musical applications, and also lays the foundation for some interesting auditory illusions. One of the most famous is the Shepard Tone, named for cognitive scientist Roger Shepard, which creates an illusion of perpetual ascent or descent. A quick search on YouTube will turn up many examples; here is a handful:

Deus Cantando — Peter Ablinger
This week’s amazing moment in timbre is a bit of a mind-bender: a piano that recreates the timbre of the human voice. It’s Peter Ablinger’s Deus Cantando (2009). for a piano being played by a computer-controlled mechanical device. Watch and be wowed:
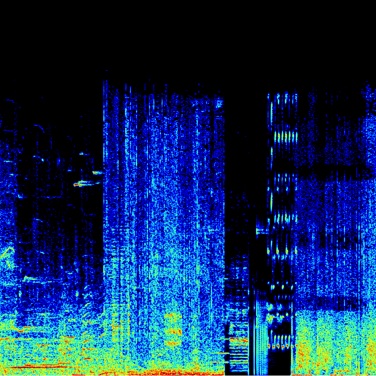
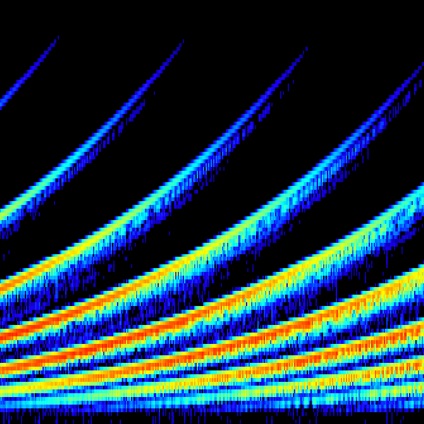
Auditory Scene Analysis
This is a spectrograph, a way of visualizing sound in which the y axis represents frequency, the x axis represents time, and darkness or colour represents concentration of energy. Looking from bottom to top shows how the sound energy is distributed on the continuum from low to high, and looking from left to right shows how that distribution changes over time...

Envelope
In synthesis and sound recording and mixing, envelope describes how a sound’s amplitude (volume) changes over time. When recreating the timbre of an instrument (or other sounds such as a firetruck siren), it is equally important to get the overtone series right as it is to reconstruct or preserve the contour of the sound….

Dripsody — Hugh Le Caine
Our second Amazing Moment in Timbre is another classic, but somewhat lesser-known. It’s Canadian composer and inventor Hugh Le Caine’s Dripsody(1955).
Atmosphères — György Ligeti
We’re beginning our “amazing moments in timbre” series with a true classic, György Ligeti’s paralyzingly beautiful orchestral masterpiece Atmosphères(1961)…

Partial
Although we may perceive sounds such as musical notes as singular, self-contained units, the physical reality often suggests something very different. Most sounds we hear are actually complex mixtures of many different sound components, some of which are noisy and transient, others of which may have stable frequencies…
